Location Services
This screen displays information about satellites that the device is currently receiving and which are used to calculate position using GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System).
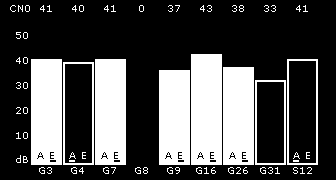
📊 Columns – signal of individual satellites
- Each vertical column represents one specific satellite.
- Column height = signal strength.
- Higher column = better reception and more accurate position determination.
- Fully filled column means the satellite is directly used for position calculation.
- Empty column – signal is received, but currently not used in the calculation.
🌍 Marks below columns – satellite system type
- G – satellites of GPS system (USA)
- E – satellites of Galileo system (Europe)
- B – satellites of BeiDou system (China)
- S – satellites of SBAS system (geostationary correction satellites, e.g. EGNOS)
What can you read from this?
- How many satellites you receive and how many of them are involved in position calculation.
- Signal quality – the higher the columns, the better the reception.
- From which systems (GPS, Galileo, BeiDou, SBAS) the signal comes.
tip
If the signal is weak or there are few satellites, try moving to a more open space without obstacles (buildings, trees).